Computer Modeling of the Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR) Process
Emerging Technology
Author: R Smith
What Is Vacuum Arc Remelting?
Remelting processes are secondary melting processes used when cleanliness and homogeneity requirements are beyond the capability of conventional production and casting processes. One such approach is vacuum arc remelting (VAR), where a starting electrode, cast from a prior production process, is gradually remelted under vacuum with heat supplied via an electric arc. The bottom of the electrode gradually melts and drips down to a molten pool, which continually solidifies, forming the final ingot. Figure 1 depicts a rough diagram and an image of VAR furnaces. There are three main parts to a VAR process: start-up, steady state, and hot top.
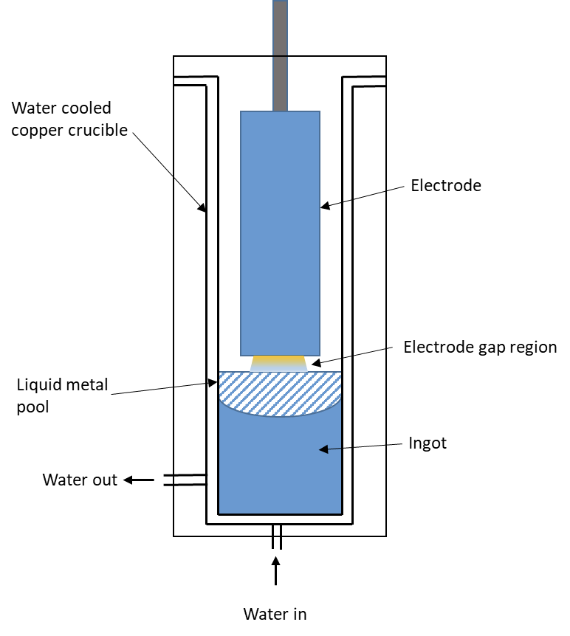 |
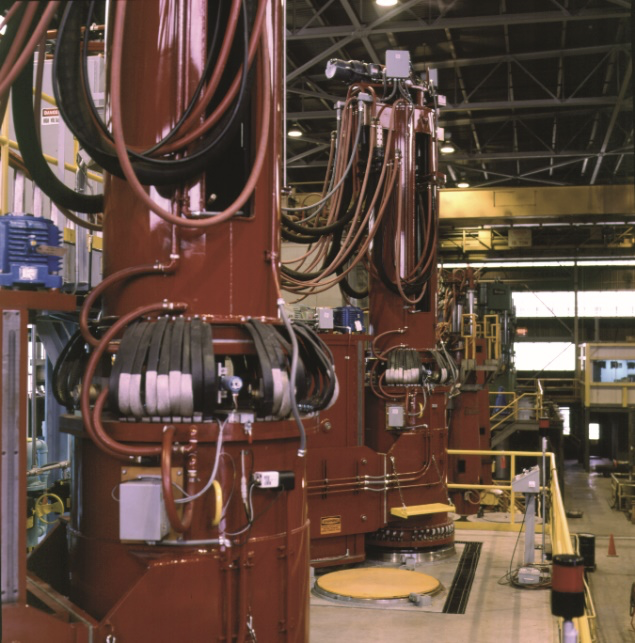 |
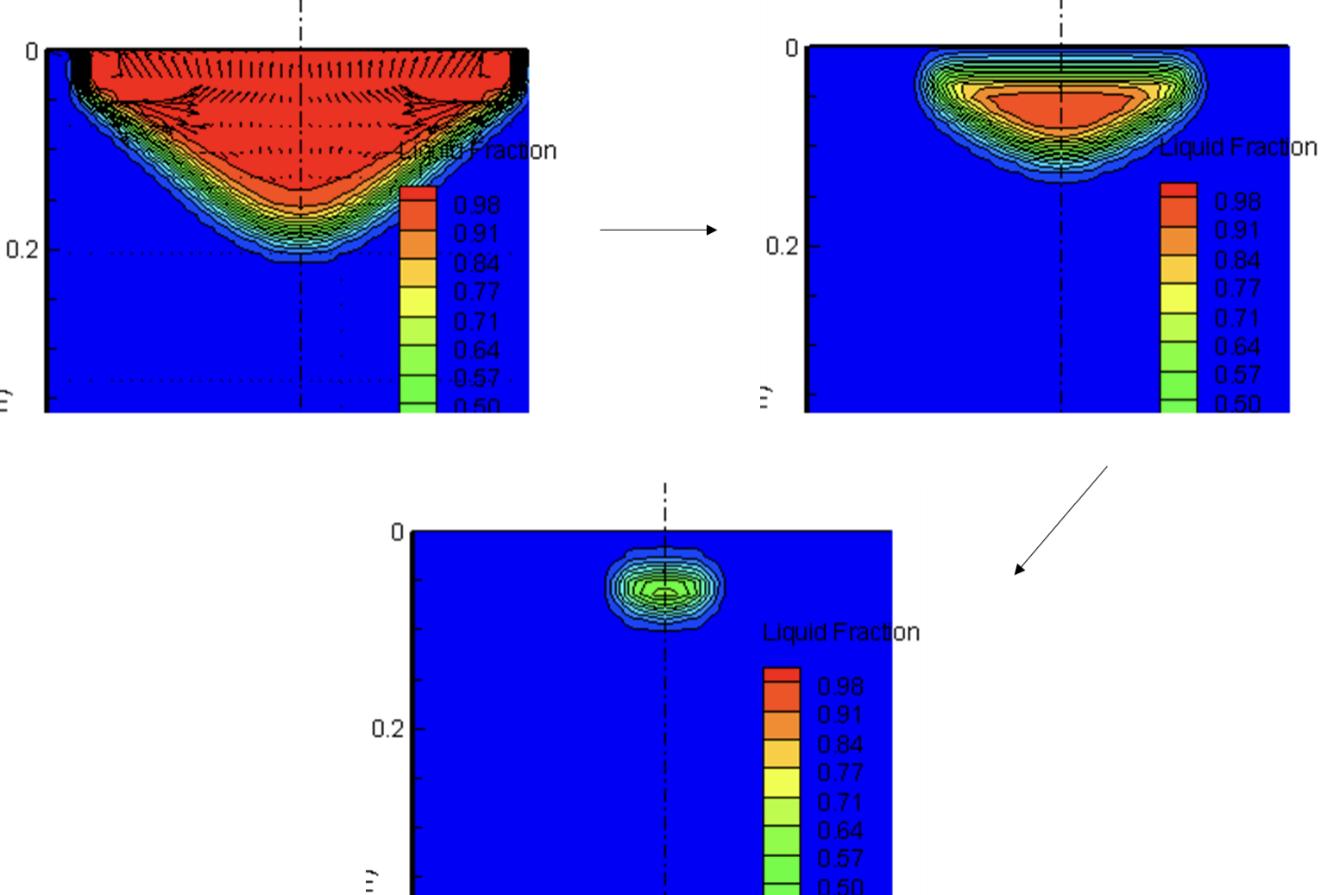
Carpenter Technology's 2D axisymmetric VAR model
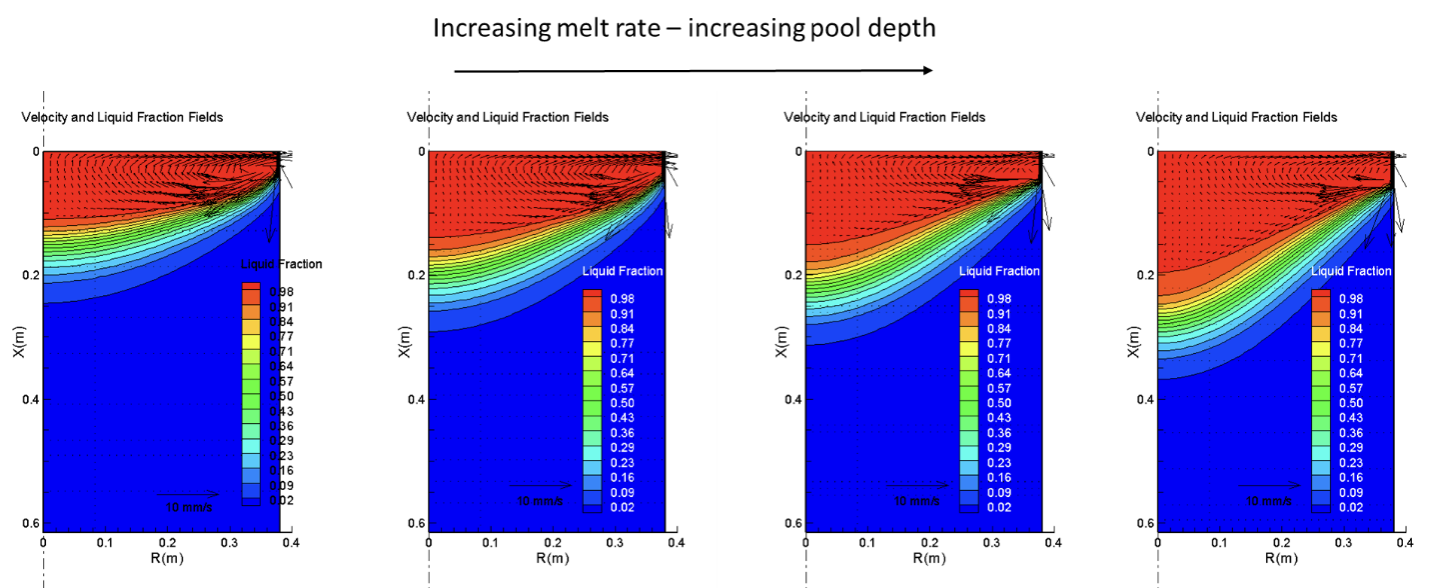
A comparison of the effect of different melt rates on pool shape is shown in Figure 4. Increasing melt rate has a visible effect on the pool's depth and shape, and these results can be used to choose a melt rate to meet desired pool conditions.
Please reach out to our expert team with any questions or inquiries.
Reference:
K.M. Kelkar, S.V. Patankar, A. Mitchell, O. Kanou, N. Fukada, K. Suzuki, “Computational Modeling of the Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR) Process Used for the Production of Ingots of Titanium Alloys”, LMPC 2007: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Nancy, France, September 2-5, 2007.